17 Effective SEO Techniques to Drive Organic Traffic in 2023
[Free Consultation] Are you spending money on advertising but not getting the results you want? Are you looking for more sales and leads but have no idea where or how to start? Get help from our world-class marketing experts in a free consultation call.
Click Here To Schedule Your Free Consultation Now
This post was updated November 2022.
Have you ever felt like SEO is a moving target?
Google makes hundreds of changes to their algorithm throughout the year, which means that what worked for last year’s – or last month’s – SEO strategy might not be adequate this year.
It can get really frustrating when your site that was doing so well suddenly isn’t. If your organic traffic isn’t coming in like before, it’s likely because there have been some tweaks on how Google views content, which can affect rankings quite drastically.
Luckily we’re here with seventeen excellent SEO techniques for 2023 to help you improve your organic search presence — covering both basic and advanced SEO techniques.
TABLE OF CONTENTS: ↓
Get My Free SEO Marketing Plan
1) AI Tools for Content Writing
One SEO strategy that will be even more popular in 2023 is using AI to write your content.
The kind of writing that an AI-powered tool can help you create includes: articles, blogs, landing pages, email copy, ad copy (Facebook Ads, Google Ads), video descriptions (YouTube), product descriptions, job descriptions, and more.
AI content writing is a process of using artificial intelligence – specifically, third-generation Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT-3), an “autoregressive language model that uses deep learning to produce human-like text” – to generate content that is both unique and relevant to your target audience.
These ever-improving AI-powered writing tools can help you create high-quality, keyword-optimized blog posts (or any other type of content) at scale. This SEO strategy for content marketing is becoming increasingly popular for good reason: With these AI writing assistants becoming more and more accurate, they can help you save time and money.
Using a GPT-3 AI tool may sound like a daunting task, but after the initial learning curve, it’s really not difficult. There are many different tools that can help you, including:
- Jasper (best for long-form content such as blog posts or landing pages)
- Copysmith (best for e-commerce content like product descriptions; allows Shopify integration)
- Rytr (best for marketing-related content like YouTube descriptions or job descriptions)
- Anyword AI (best for copywriting content like ad copy)
These tools uses artificial intelligence to help you write better content by understanding the topic that you’re writing about, doing some of the research for you, and then suggesting related headers or sections that you may want to include.
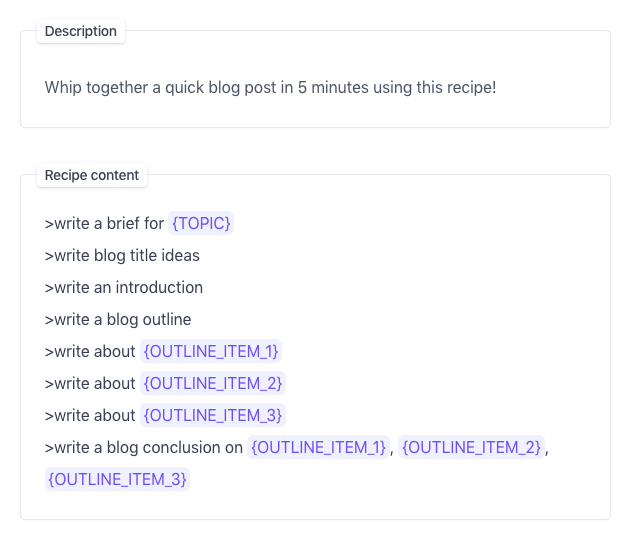
For instance, to write a blog post, a tool like Jasper can:
- Suggest topics that are relevant to your audience
- Create a brief and an outline
- Come up with several choices for an article headline
- Provide a list of items for your listicle
- Write your introduction, conclusion or any paragraphs in between
- Craft a meta description for your article
Here’s how it works: You provide the AI content writer with a topic/keyword and some basic information about what you want to cover. The more specific you are, the more specific the output will be.
The AI writing tool then does research on the topic and creates a draft of the article – all within seconds. You then review the draft and make any necessary changes before publishing it on your site.
Note: It’s important to run your finished draft through Copyscape to make sure your AI tool hasn’t inadvertently plagiarized someone else’s hard work.
Using an AI-powered tool to create your content helps you improve your SEO as it can generate content that is optimized for specific keywords. As a result, your content is more likely to rank higher in the search engine results pages (SERPs).
Check out Single Grain founder Eric Siu’s short video How to win at SEO for 2023 & Beyond:
Learn More: 10 Easy Ways to Get Started with Marketing AI (Artificial Intelligence)
2) App Store Optimization for Mobile SEO
App store optimization (ASO) is an SEO strategy that focuses on optimizing mobile apps in order to gain a higher ranking in an app store’s search results. The goal of ASO is to improve the visibility of an app in order to attract more downloads and, ultimately, generate more revenue.
ASO is similar to search engine optimization (SEO) for websites. Just as SEO helps website owners improve their visibility in Google’s search results, ASO helps app owners improve their visibility in Apple’s App Store or Google Play’s search results.
There are two main ways to optimize an app for better visibility in the app store:
- Improve the app’s metadata. This includes the app’s title, description, keywords, and screenshots.
- Improve the app’s rating and reviews. This can be done by encouraging users to leave positive reviews and by responding to negative reviews in a constructive way.
Five tips for App store optimization:
- Use keyword-rich titles: The title of your app is one of the most important ASO factors, so make sure to include relevant keywords.
- Use keyword-rich descriptions: Just like your app’s title, its description is also an important ASO factor. Make sure to include relevant keywords and write a description that is both informative and appealing.
- Use keyword-rich keywords: In order to improve your app’s visibility, you need to include relevant keywords in the keyword field. But don’t stuff your keywords – only use them if they are truly relevant.
- Encourage positive reviews: One way to improve your app’s rating and visibility is by encouraging users to leave positive reviews. You can do this by providing an incentive, such as a discount or coupon code.
- Optimize your app’s screenshots: The app screenshots are one of the first things that users see when they view your app’s listing, so make sure to choose high-quality images that accurately represent your app:
Here are the guidelines for the Google Play and Apple iOS stores:
Google Play
- Title: up to 30 characters
- Short description: up to 80 characters
- Description: up to 4,000 characters
- Google Play indexes nearly all of the text that is included in the store listing.
Apple (iOS) App Store
- Title: up to 30 characters
- Subtitle: up to 30 characters
- Keywords field: up to 100 characters
- The iOS app store doesn’t index all text fields (unlike Google), so try to get your keywords in these additional fields:
- Developer name
- In-app purchases (IAP)
Learn More: App Store Optimization (ASO) Strategies for New Mobile Apps
3) Implement Content Optimization Right Away
For most people, SEO entails publishing content regularly, targeting new keywords and getting links to those pages.
But experienced SEO practitioners know that you can increase your organic traffic more strategically by optimizing your existing content through a process known as “content optimization.”
Content optimization aims to optimize a page’s on-site meta tags like:
- Including primary and secondary keywords at the correct densities
- Having an appropriate word count
- Ensuring great readability
- Having optimal meta title and description tags
Here are four ways you can implement content optimization throughout your site easily and quickly.
A) Find Appropriate Word Counts and Keyword Densities
Every SERP is different. Some queries are answered immediately in a featured snippet, whereas others are best served with 500-1,000-word sales pages. Then there are queries that require in-depth articles of 3,000+ words.
That’s all to say that there’s no right or wrong word count to aim for, as it’s purely contextual on the search query and its top-ranking pages. However, if you get this wrong, you’ll find it very difficult to rank.
B) Test Your Meta Titles to Optimize CTR
Title tags are one of the most important on-site tags to optimize a page for. Meta descriptions? Not so much. However, just because Google doesn’t look at a meta description to rank a page, it doesn’t mean they don’t matter.
A great meta description can give you a CTR boost, which can lead to higher rankings. Several years ago, Rand Fishkin described how Google might approach it during a Whiteboard Friday episode: “If the position four result is getting more clicks than the position two result, shouldn’t they be switched around?” Other reputable sources such as CXL have also concluded that CTR is a ranking factor.
Dive Deeper:
* What Is Content Decay and How It Affects Your SEO
* How to Write Hero Headlines to Skyrocket Click-Through Rates
C) Identify Pages with Declining Traffic Using Content Decay
As you publish more content, traffic and rankings from your old content inevitably start to slip.
Posts become outdated, competitors update their articles, you stop building new links, and so on. Whatever the reason, it’s tricky to keep everything up to date while also pursuing new topics.
Addressing your decaying traffic is one of the easiest ways to keep track of your older (but still valuable) content and prioritize where to spend resources on updating old posts compared to creating new content.
Dive Deeper: Content Decay Masterclass: How to Double Your Blog Traffic by Refreshing Old Content
D) Cover Related Questions to Align with Search Intent
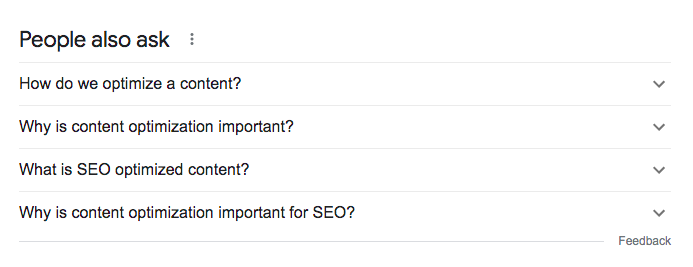
The “People Also Ask” and “Related Searches” sections in the SERPs are two magnificent tools you can use to uncover a user’s search intent.
For example, if you’re looking to rank for the keyword “content optimization,” you may be tempted to write a long tutorial on the subject (like this article). By answering the questions you find in the “People Also Ask” section, you may be able to drive some of the voice-assisted searches we mentioned earlier:
The “Related Searches” section at the bottom of the SERPs can also give you some suggestions as to what sections you could include in your article.
For each topic, you can navigate to the “Research” tab to display a list of also-searched questions.
Get My Free SEO Marketing Plan
4) Provide a Flawless Page Experience
Page site optimization has been a relatively weak ranking factor, which, naturally, SEO practitioners never took too seriously. Sure, it mattered, but not more than traditional on-site optimization and good ol’ link building.
Life in the SEO world moves pretty fast though. With the launch of BERT and MUM, the latest SEO trends show that Google wants to humanize its search engine by gearing its ranking algorithm towards metrics like, you guessed it, page site optimization.
Links and tags matter — and will continue to do so for as long as we can see — but they aren’t the only things to look out for. With the 2020 launch of the Page Experience Update, Google made this new metric a core part of its algorithm.
Google defines page experience as:
“a set of signals that measure how users perceive the experience of interacting with a web page beyond its pure information value.”
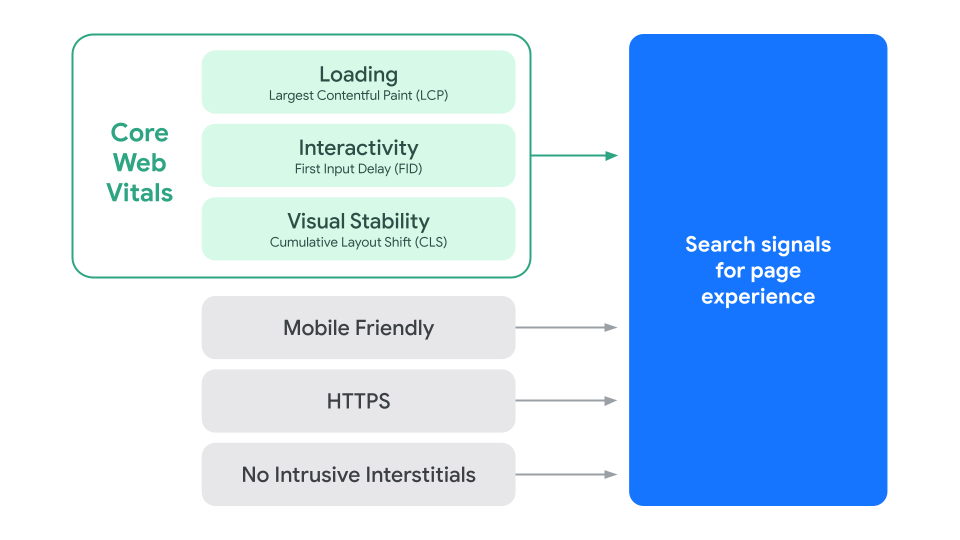
Let’s be clear about something: Google has no way of knowing how users truly perceive a web page (although Elon Musk’s Neuralink may change that soon). Instead, they take four metrics that correlate with a page experience and make educated guesses.
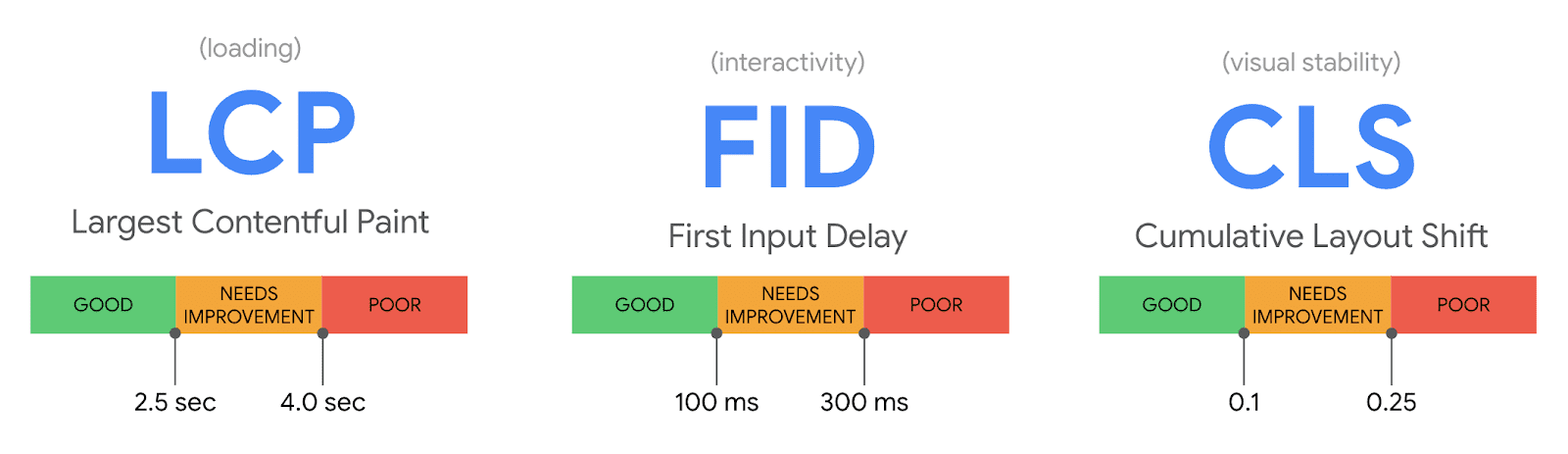
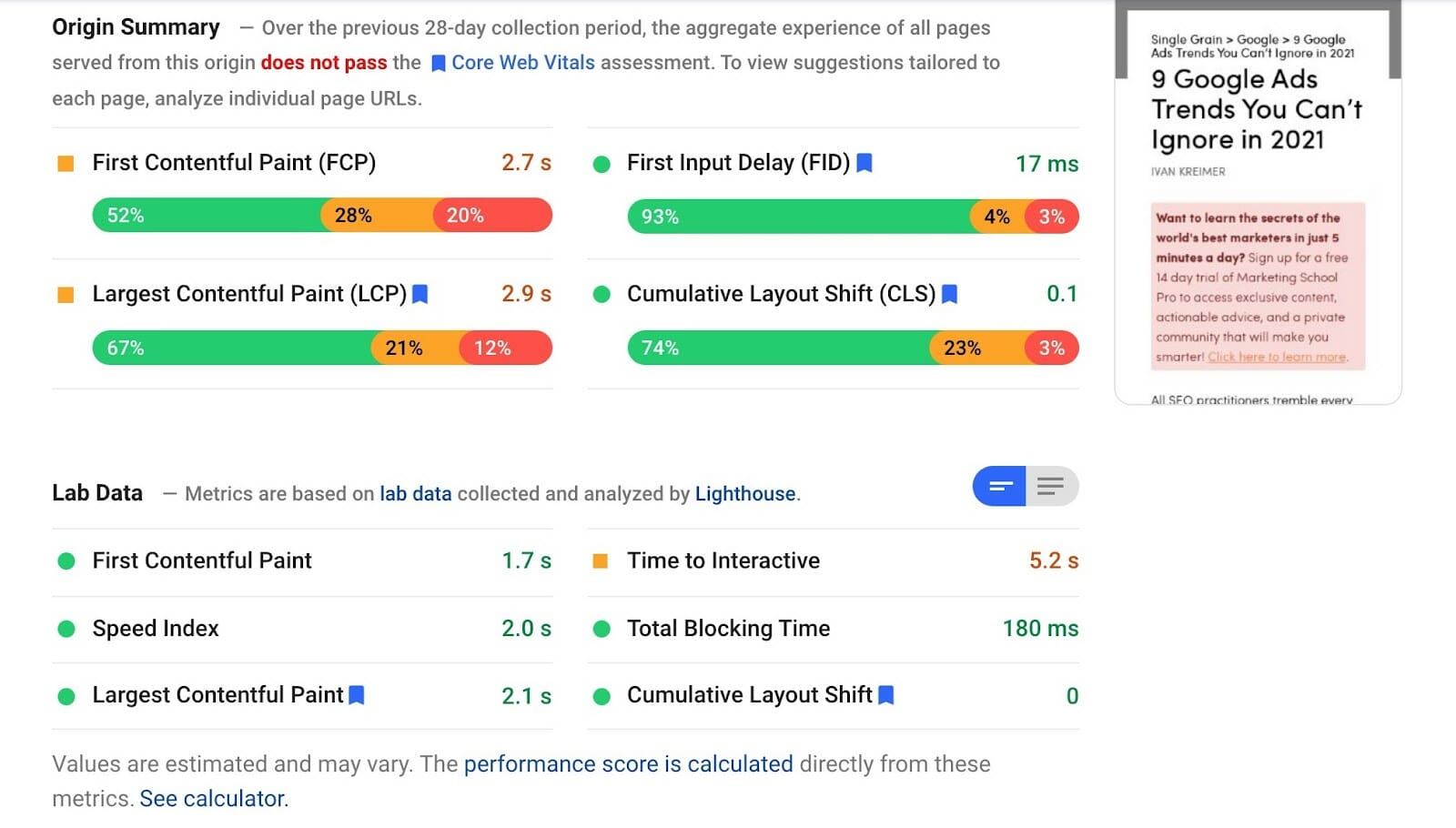
The first metric is the Core Web Vitals, an amalgamation of metrics that measure a page’s load speed from a user experience perspective:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. Google recommends aiming for an LCP under 2.5 seconds after a page starts to load.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity. Google recommends an FID of less than 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability. Google recommends a CLS score of less than 0.1.
The other three metrics are a page’s mobile friendliness, the use of the HTTPS protocol, and the lack of intrusive interstitials:
If you haven’t paid any attention to your page experience, then here’s what you need to do.
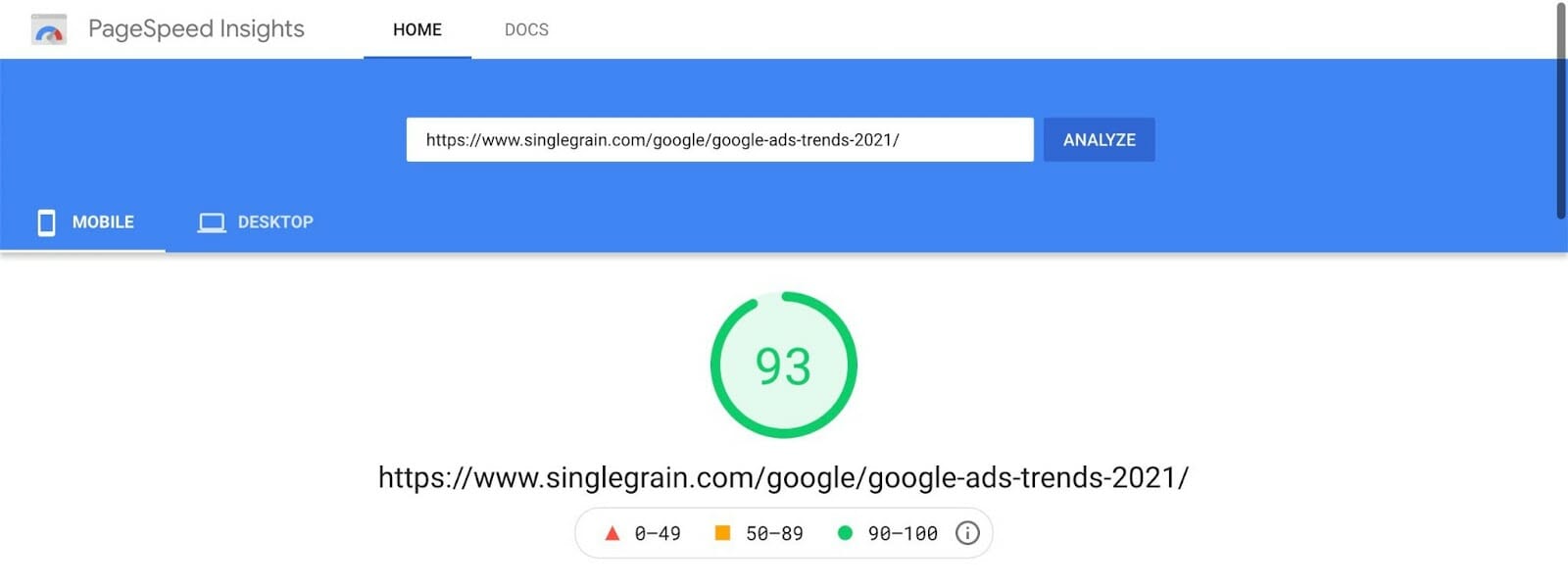
- First, run your website through PageSpeed Insights to gauge how it performs against the Core Web Vitals:
- Then take note of the recommendations Google gives you below the fold to improve any issues you may find:
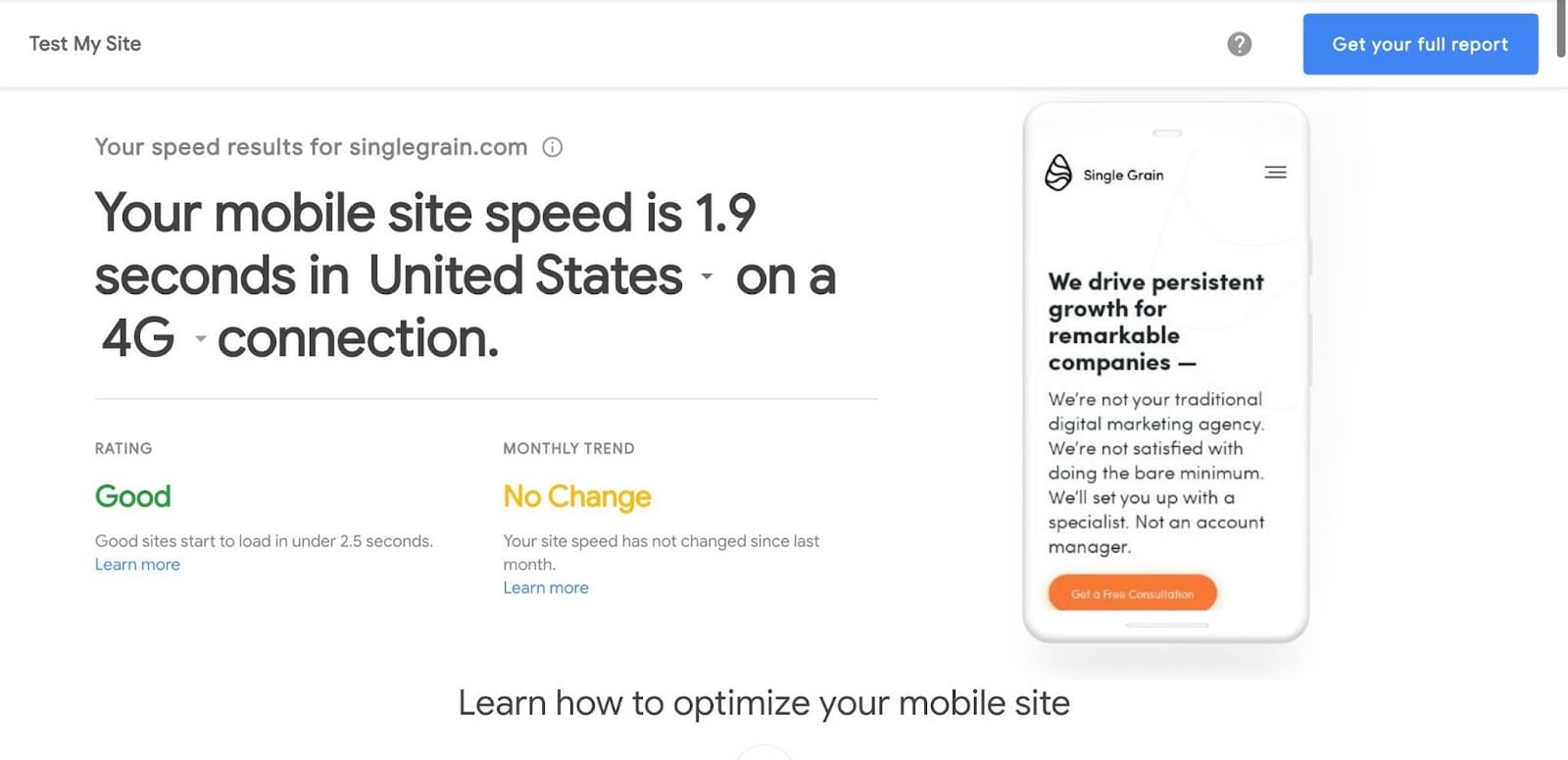
- Repeat the process with Test My Site to measure the responsiveness for your site:
Boosting page speed can do more than improve organic performance; it can also increase conversions.
One survey found that nearly 70% of consumers said that page speed affects how willing they are to buy from a website.
Here are a few ways you can boost page speed for better rankings and more conversions:
- Minify unnecessary code on your page
- Defer JavaScript loading
- Reduce server response time
- Choose the right hosting option for your needs
- Enable browser caching
- Enable compression
- Compress images to cut down page size by 30-40%
Once you have finished boosting your site speed, make sure your site meets the other three criteria that make an optimal page experience:
- Make your website mobile-friendly
- Buy an HTTPS certificate for your domain
- Remove all unnecessary pop-ups (the ones you use to build an email list probably don’t qualify as problematic; the ones that open new tabs or windows are)
Dive Deeper:
* How to Write Content for People and Optimize It for Google
* How to Prepare Your Site for the New Page Experience Update
* CWV Update: Why Google Keeps Changing How It Measures Your Site’s UX (and What to Do About It)
5) Increase Your Dwell Time
The SEO industry has speculated forever about the impact of user experience in Google’s ranking algorithm. Yes, a clean site architecture, a fast load speed, and mobile experience are important, but none of these factors truly had a strong effect on rankings…until recently.
As you may have guessed, the almighty Google once again decided to flip the switch and make one aspect of user experience critical within their suite of ranking factors: dwell time.
Before you can say I misspelled bounce rate, let me give you a rough definition:
Dwell time is the time a visitor spends looking at a page after they click on a SERP link and before they go back to the SERPs.
Let’s think of it with the following example:
- A Google user searches with the keyword “SEO techniques,” checks the top results, finds this page, and clicks on it.
- Four minutes and 35 seconds later, the user decides that they found what they were looking for and goes back to the SERPs to read other pages.
Their dwell time would be 4 minutes and 35 seconds. On its own, this benchmark doesn’t make much of a difference to you or Google. But if Google thinks that people stay longer on this page than on our competitors’ pages, they will figure out that our page is probably doing something better.
The happier the users, the better it is for Google. Therefore, they will reward the high dwell time page over its competitors. How much? We don’t know. But it may be the extra nudge a page needs to steal a number one position for a highly competitive keyword.
To be clear: Dwell time isn’t the same as bounce rate, as the latter measures the number of visitors who land on a page and then leave without any other interaction. More specifically, it’s the percentage of single-page sessions divided by all the sessions for your website (or an individual page).
Bounces, like good ice creams, come in different flavors: some come from visitors via Twitter, others from direct sources (like bookmarks), and so on.
Dwell time isn’t time on site either, as the latter can include people who came from outside the SERPs. Dwell time is like the offspring of bounce rate and time on site, but way more SEO-friendly than its parents.
The bad news is that you can’t do much to improve your dwell time — except improve your user experience. Anything that makes your website more user-friendly will likely increase your dwell time. And the opposite is true, too: If your website looks untrustworthy, outdated or amateurish, new visitors are likely to bounce back to the SERPs and click on another result. And Google won’t like that.
Now that you understand dwell time, here are a couple SEO techniques you can use to improve user experience and give your existing content a boost in search engines.
A) Make Your Posts Easy to Read
Ever heard the phrase “formatting content for the web”? To stand any chance at increasing your organic rankings, you need to take that a step further and optimize content for readability.
These formatting tips can help increase the readability of your content:
- Write quality content: Formatting matters, but so do great ideas, compelling delivery and error-free grammar and spelling.
- Use short paragraphs: Aim for paragraphs of 3-4 sentences long. If necessary, you can even use one-sentence paragraphs, but use them sparingly or your post will look like a grocery list.
- Mix sentence lengths: Long sentences are hard to follow on a computer or mobile device, but they can work well when used sparingly — particularly when mixed with shorter sentences. Here’s a fantastic example of how sentence structures can be varied for optimum readability (the Hemingway app can help with this):
- Sub-headers: Did you know that the average person spends just 37 seconds reading a piece of online content? You can significantly boost that time by including subheadings that help readers scan content and quickly understand what the article is about.
- Bullet points: When you have a lot of data — stats, facts, ideas, examples — packed into one paragraph, it makes it easier to read when you list them with bullet points (like this one!). As a rule of thumb, use bullet points whenever you list three or more items.
- Use white space: Break up large chunks of text with relevant, supporting media, including photos, videos, and graphs (in addition to bullet points and sub-headers).
- Use images and screenshots: Most articles should have several images or screenshots to illustrate the points or numbers or steps you are discussing. The more complex the idea, the more images you should include. (Imagine this entire blog post without any images. It would be daunting, right?)
Dive Deeper: 7 Mistakes in UI and UX That Are Costing You Engagement
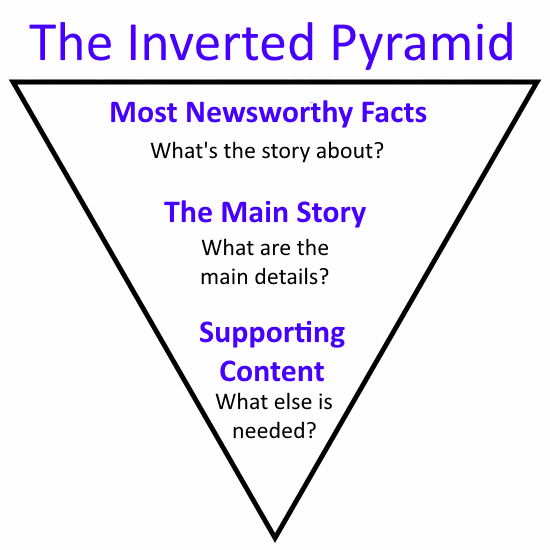
B) Use the Inverted Pyramid Style of Writing
One of the basic rules of journalists is the inverted pyramid style of writing, which looks like this:
In this pyramid, the most valuable information is at the top of the article, with less important information appearing below. Readers that scan articles rarely reach the bottom of the page, so it makes sense to give them what they want as soon as they land.
Get My Free SEO Marketing Plan
6) Focus on Topic Clusters Instead of Keywords
Google is evolving and so is its algorithm. Its objective now is to understand the intention of its users — what they expect, what they’re looking for and, more specifically, what search results would best help answer their query.
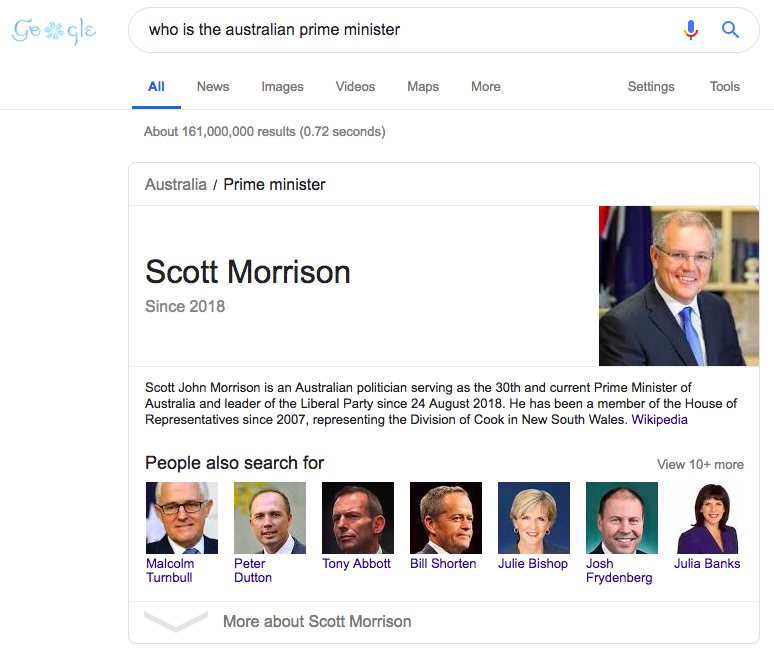
That’s where the featured snippet box comes into play…again:
However, don’t expect your website to appear on the first page of Google simply by creating keyword-focused content. It’s not enough to look at keywords alone; we need to look at the context around them. Also referred to as “user intent,” you must pay attention to what your users are looking for.
Here are two things in particular you should consider:
A) Know Your Target Audience
The type of content you’ll create will depend entirely on your audience. The better you know them — their location, age, interests, etc. — the better the content you’ll create (and the better your SEO).
For example, suppose your keyword tool shows that “Android” has a search volume of 2,740,000 per month. That’s a lot of people your content could be exposed to, so you’ll need to target it heavily, right? Not necessarily.
People searching for “Android” could fall into several categories:
- Mobile users searching for Android help
- Star Wars fans looking for droids
- Robotics enthusiasts looking for information about Androids
If you don’t understand your target audience, you could risk creating content for all these topics. That won’t win you rankings or readers because you can’t please everyone with a single piece of content optimized for such a broad term.
However, by building buyer personas that include the shared traits of your ideal customers, you’ll be better able to zero in on topics that matter to your readers, while also minimizing the chances of creating content that fails to get results.
Dive Deeper: The Ultimate Guide to Developing Buyer Personas (with Templates!)
B) Organize Content into Clusters
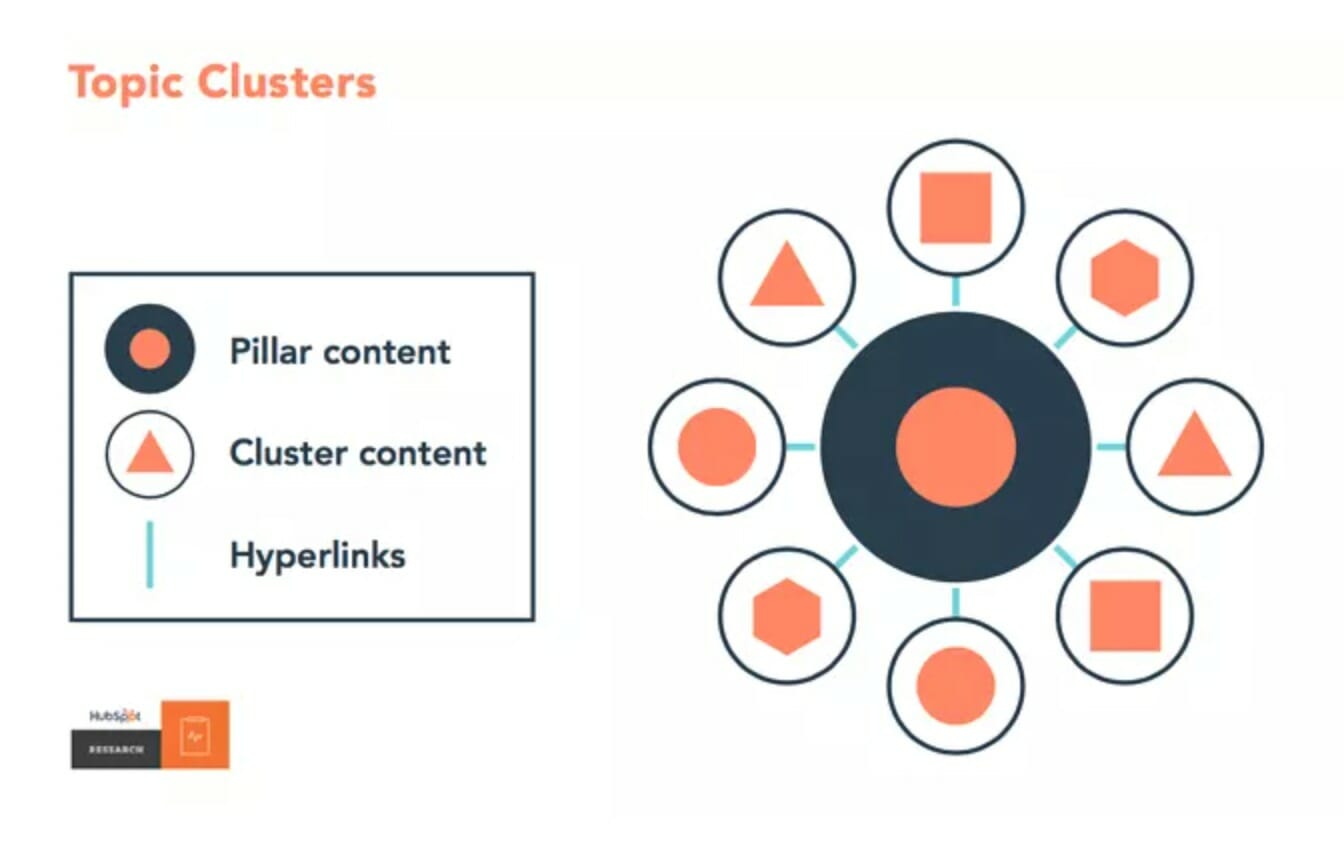
Instead of focusing on standalone keywords, organize all your content into different themes. The topic cluster model, created by HubSpot, works by linking relevant content pieces together into “clusters”:
This entails having:
- A pillar page: These are generally your site’s most important pages (for example, on an e-commerce site, this will often be top-level categories) that you want, and can expect, to rank for a broad range of keywords.
- Cluster pages: These are pages that live around and are linked back to their relevant pillar page. They will generally answer questions or cover topics related to the pillar page in more detail.
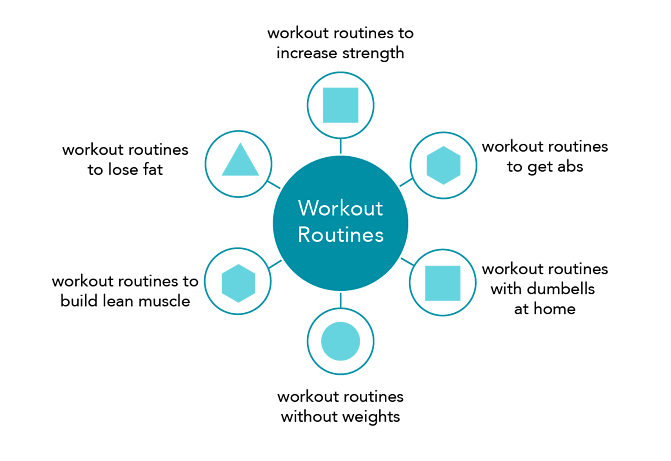
Here’s a topic cluster around “workout routines”:
This strategy achieves three things:
- It satisfies user intent since they get easy access to more detailed information on their topic of interest.
- It turns your site into a better resource for those pillar topics. This is important to Google, since its goal is to send users to the best possible page for their search term. When Google views your site as a great resource for a particular topic, odds are you’ll be rewarded with better rankings.
- Each of those cluster pages has the potential to rank themselves, and drive additional traffic to your site.
Dive Deeper:
* 5 Steps to Developing Successful Pillar Content
* Quick Guide to Using Topic Clusters to Improve Your SEO
C) Do Your Keyword Research
Wondering why we’re listing keyword research as an SEO technique when we’ve told you to focus on topic clusters, rather than keywords?
Because keywords still matter.
Organizing content thematically is key, but it’s a mistake to ignore keywords entirely. Keywords act as signposts to Google’s spiders, signaling topics and providing hints as to the nature of the content on the website. By doing keyword research, you discover who is searching for the topics you want to write about, and so it’s easier to create blog posts or other types of content that answers customers’ specific questions and increase brand recognition.
There are many tools you can use to access keyword data:
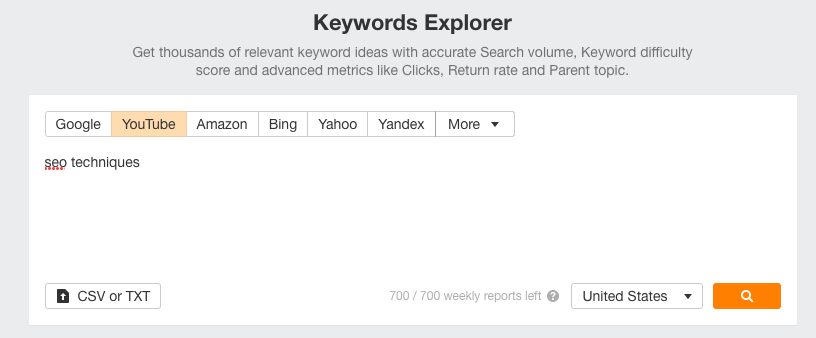
- Keyword Explorer by Moz: Keyword Explorer is a versatile, dynamic program that covers nearly every aspect of the process. It helps marketers brainstorm keywords, build lists and filter them by topic. You can also analyze metrics, click-through rates and other measures of effectiveness, as well as spy on and assess keywords used by your business rivals.
- SEMrush: SEMrush is widely regarded as one the best tools for SEO analysis, particularly where it concerns business intelligence. One of its many features allows you to identify and analyze the keywords your competitors are using simply by entering your competitor’s URL into the SEMrush search bar.
- Ahrefs: Ahrefs offers a wide range of products, including backlink checkers, content explorers and position trackers. In this post, we’ll focus on their Keywords Explorer, which lets marketers search nearly 7 billion keywords in over 170 countries, assessing metrics like keyword difficulty, click-through rates, related keyword lists, and search volume:
Using Semantic Keywords
What are semantic keywords?
Semantic keywords are words and phrases that are related to your primary keyword. They help search engines understand the context of your content and improve its relevancy for certain queries.
For example, if you’re writing an article about “SEO techniques,” some relevant semantic keywords could be “content marketing,” “link building,” or “on-page SEO.”
The reason they are important is that using semantic keywords in your content can help you rank for more long-tail keywords. And as we all know (or as you now know), ranking for long-tail keywords is essential for driving organic traffic to your website!
There are a few different ways to find relevant semantic keywords for your content.
One way is to use Google’s “searches related to” feature. Simply enter your primary keyword into Google and scroll to the bottom of the page. There, you’ll see a list of related searches that you can use as semantic keywords:
Another way is to use a tool like Semrush. Just enter your primary keyword into the Keyword Magic Tool and click on the “Questions” filter in the left-hand sidebar. This will show you a list of all the questions that people are searching for that are related to your primary keyword.
Check out this 5-minute video How to Use Ahrefs for SEO Analysis:
Note: Even if you use an Ahrefs alternative like Semrush, SE Ranking or Mangools, this process is similar.
Dive Deeper:
* SEO Keyword Research Made Easy
* How to Use Google Keyword Planner for Content Creation
* Why You Should Use Long-Tail Keywords in Your SEO Campaign
7) Create Voice Assistant-Friendly Content
Do you write as you speak? Maybe you do when you chat with your friends over WhatsApp, but not usually when you are at work. And do you search in Google as you speak? Once again, you likely don’t.
However, with the advent of voice assistants, that’s no longer the case. Now that 4.2 billion voice assistants are being used worldwide (a number estimated to hit 8.4 by 2024), searches have become more fluent, conversational, and complex for Google. And in a more conversational search engine world, you must optimize your website for voice search.
Here’s how you do it:
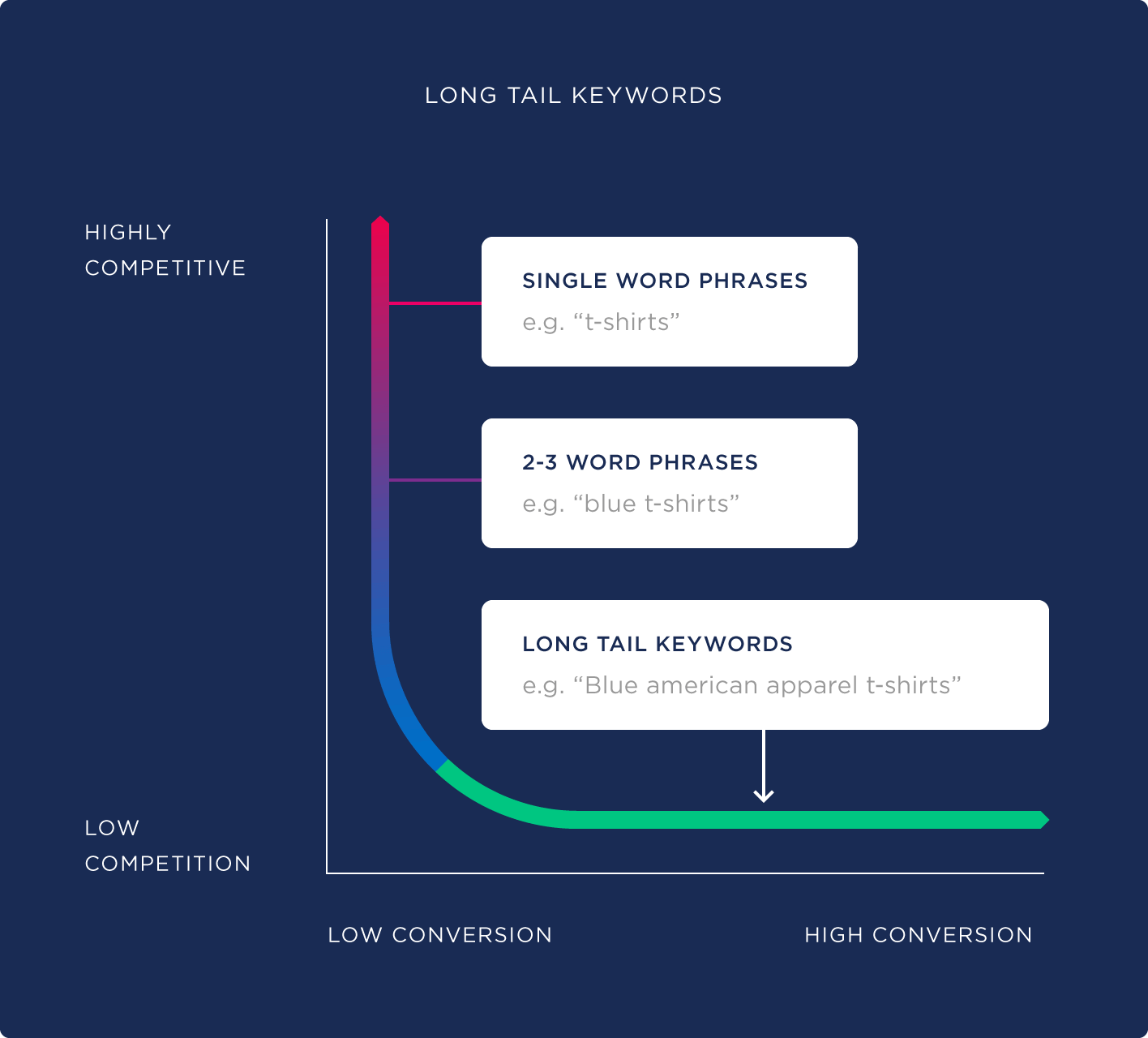
A) Use Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords — those that contain three or more words — play a key role in voice search. To rank for this type of keyword, you’ll need to create content that targets them on your website using the following process:
- Identify one long-tail keyword using this guide (e.g. “how to wash a car”).
- Find lots of semantically related keywords (e.g. “car washing guide” and “best soap for washing a car”).
- Write a long-form, comprehensive blog post that suitably positions those semantically related keywords throughout.
B) Use Structured Data
According to Backlinko, 40% of voice search results come from featured snippets. Using structured data can help boost the chances of your content being used to answer a voice query over a competitor’s.
As Ana Gotter explains:
“Schema markups are often used to point to local businesses with snippets of code in order to help Google understand what your website is about and thus better connect you with relevant searches.”
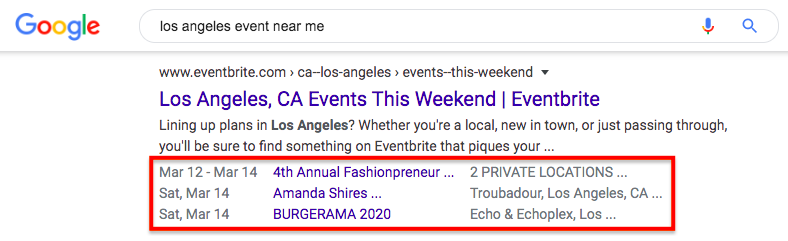
Here’s an example of how web pages with schema markup for events appear in the SERPs:
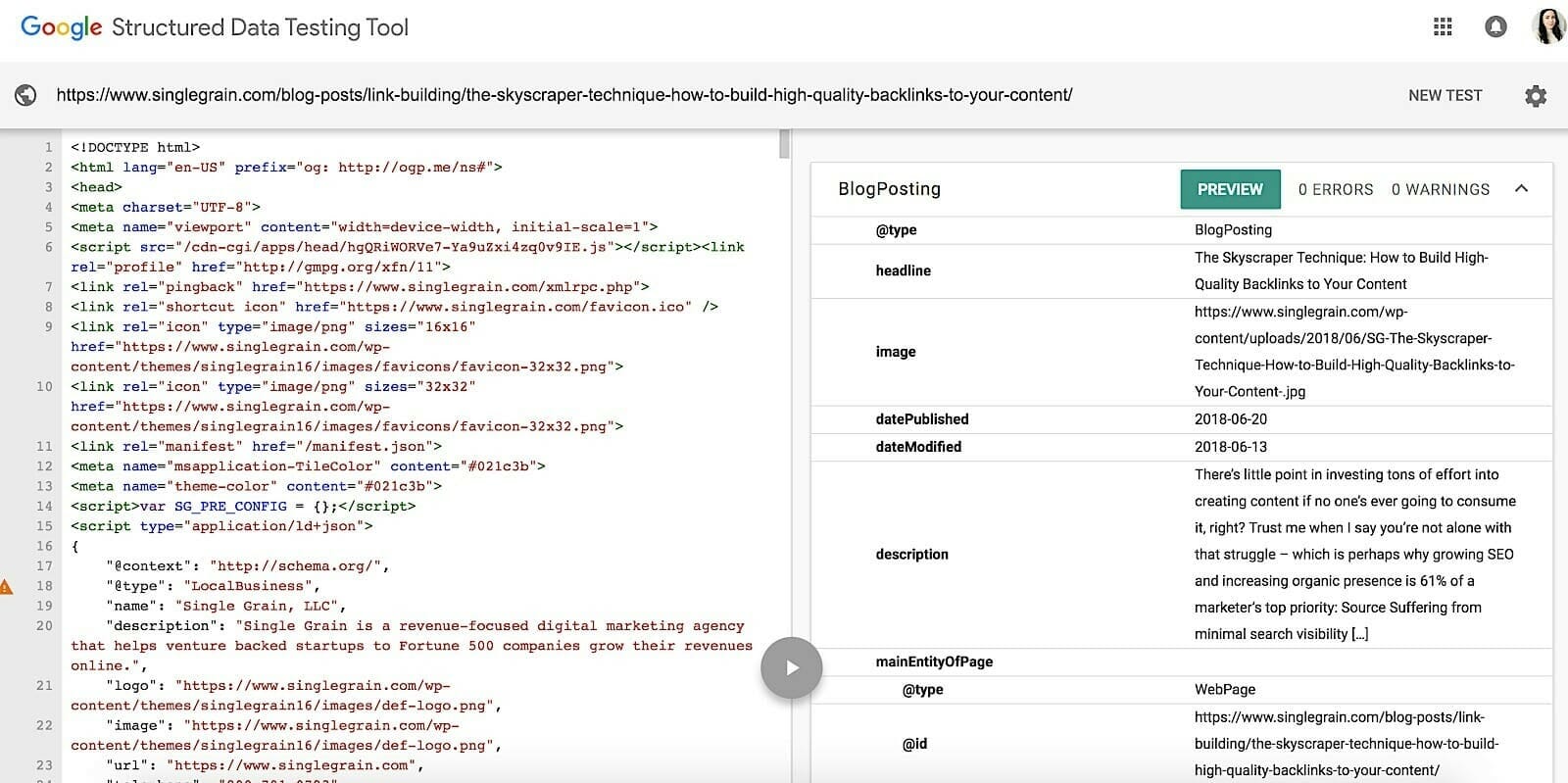
To get started, head over to Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to find out whether you’ve already implemented schema:
If you haven’t and you need more detailed information, check out Google’s guide to Schema markup that explains the type of code you need, and how to implement it.
Dive Deeper:
* Beginner’s Guide to Voice Search SEO
* How to Optimize Your Website for Voice Search and Wearable Tech
8) Optimize Your Headings (Not Just Your Title Tags!)
There’s a moment in the life of any SEO practitioner where they look at the sky in despair and scream: “Why Google? Why?!”
That happened recently when the SEO industry was shocked to find that Google launched the “page title update” in which they started to automatically rewrite title tags based on a page’s H1 heading.
Anyone seeing massive title rewrite on Google? Been noticing it on multiple SERPs for multiple keywords that Google is either pulling H1 or H2 to use for title.@rustybrick #SEO #searchengineoptimization #Google
— Jackie Owen (@techjackie) August 17, 2021
Although industry veterans like Danny Sullivan said that this practice isn’t new, the change still shocked many professionals. At first, people were confused but skeptical about the lasting effects of this change.
Then, on August 24, Google came forward about their web page title update, explaining that their “new system is producing titles that work better for documents overall, to describe what they are about, regardless of the particular query.”
On August 25, Dr. Peter J. Meyers of Moz analyzed the SERPs for 10,000 keywords and discovered that of 57,832 title tags, 33,733 had been rewritten – that’s 58%! Although a large chunk of these rewrites happened due to “natural” reasons, such as when Google truncates an overly lengthy title, many were victims of Google’s strange workings.
Here’s one example from MailChimp’s home page, which looks like this:
Compare that basic, SEO-unfriendly title tag with its true SEO-friendly counterpart, and you will see the difference:
According to Brodie Clark, Google is replacing titles with “header tags, internal links, image alt text, or even made up completely by Google.”
Like most SEO-related challenges, there’s no way to know when or how Google will rewrite your title tags. However, in their update release, they indicated that they are most likely to change a tag if it’s:
- Exceedingly long
- Keyword-stuffed
- Lack title tags entirely or contain repetitive “boilerplate” language, such as home pages called “Home”
To calm everybody down, Google says that:
“our main advice on that page to site owners remains the same. Focus on creating great HTML title tags. Of all the ways we generate titles, content from HTML title tags is still by far the most likely used, more than 80% of the time.”
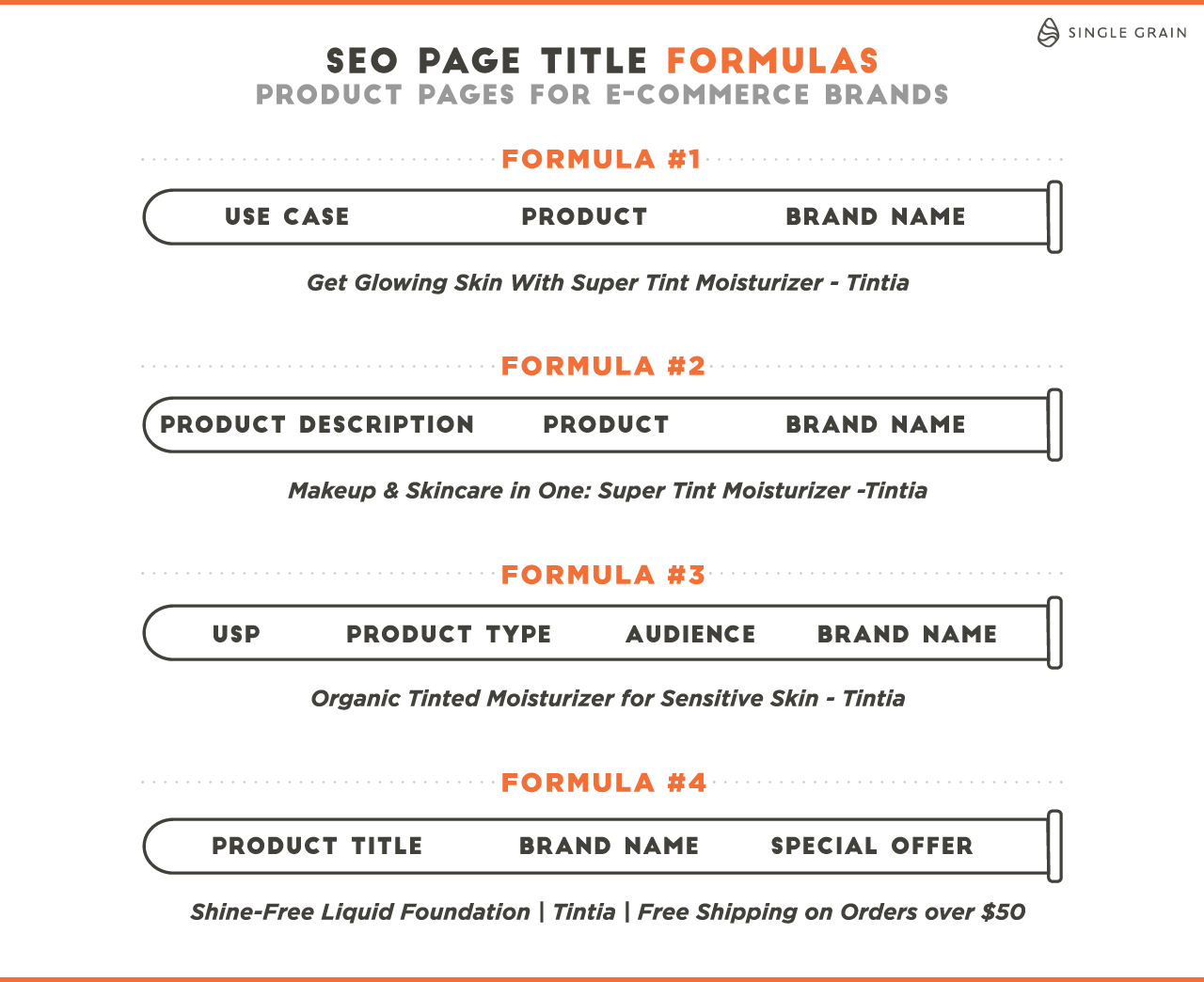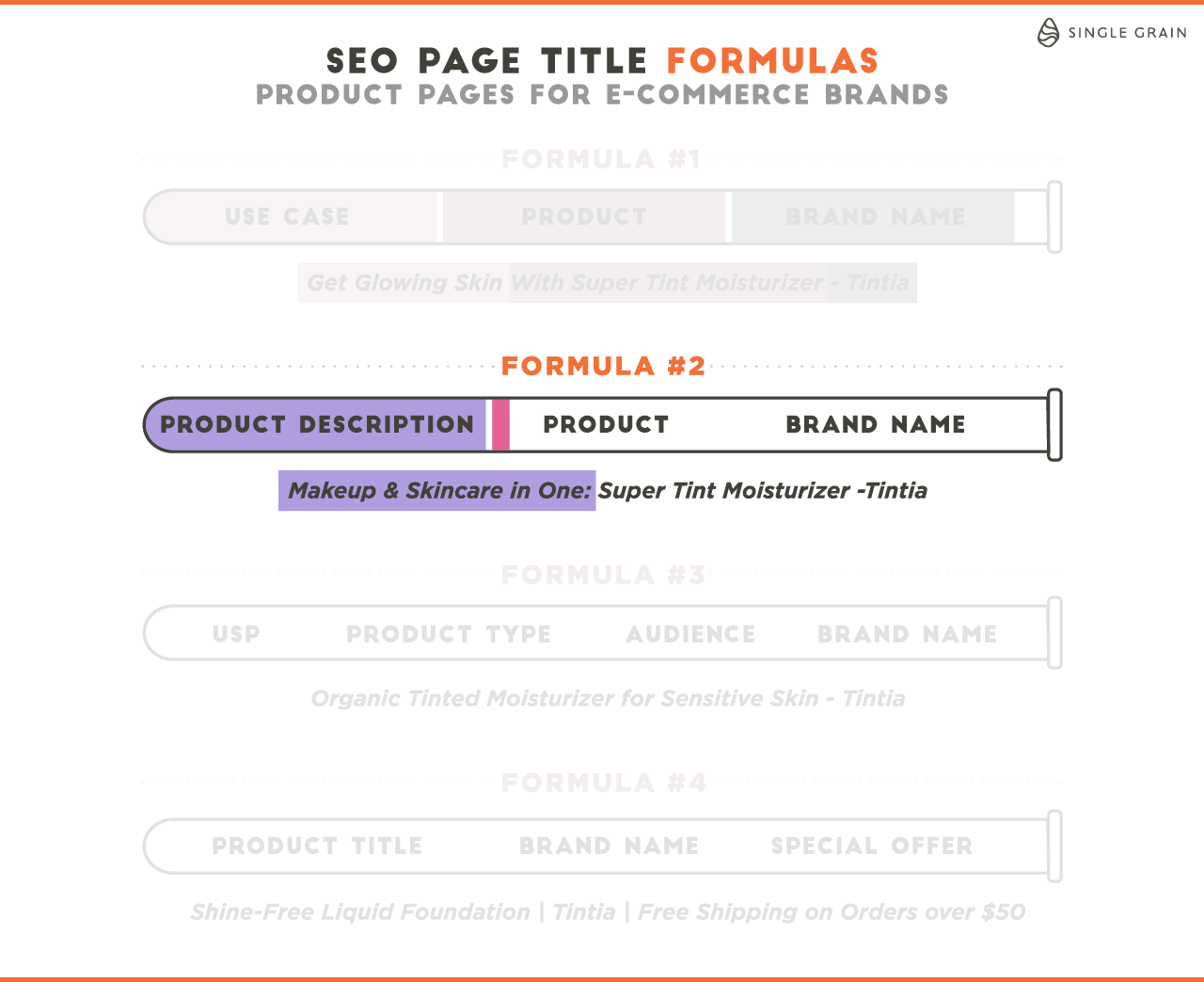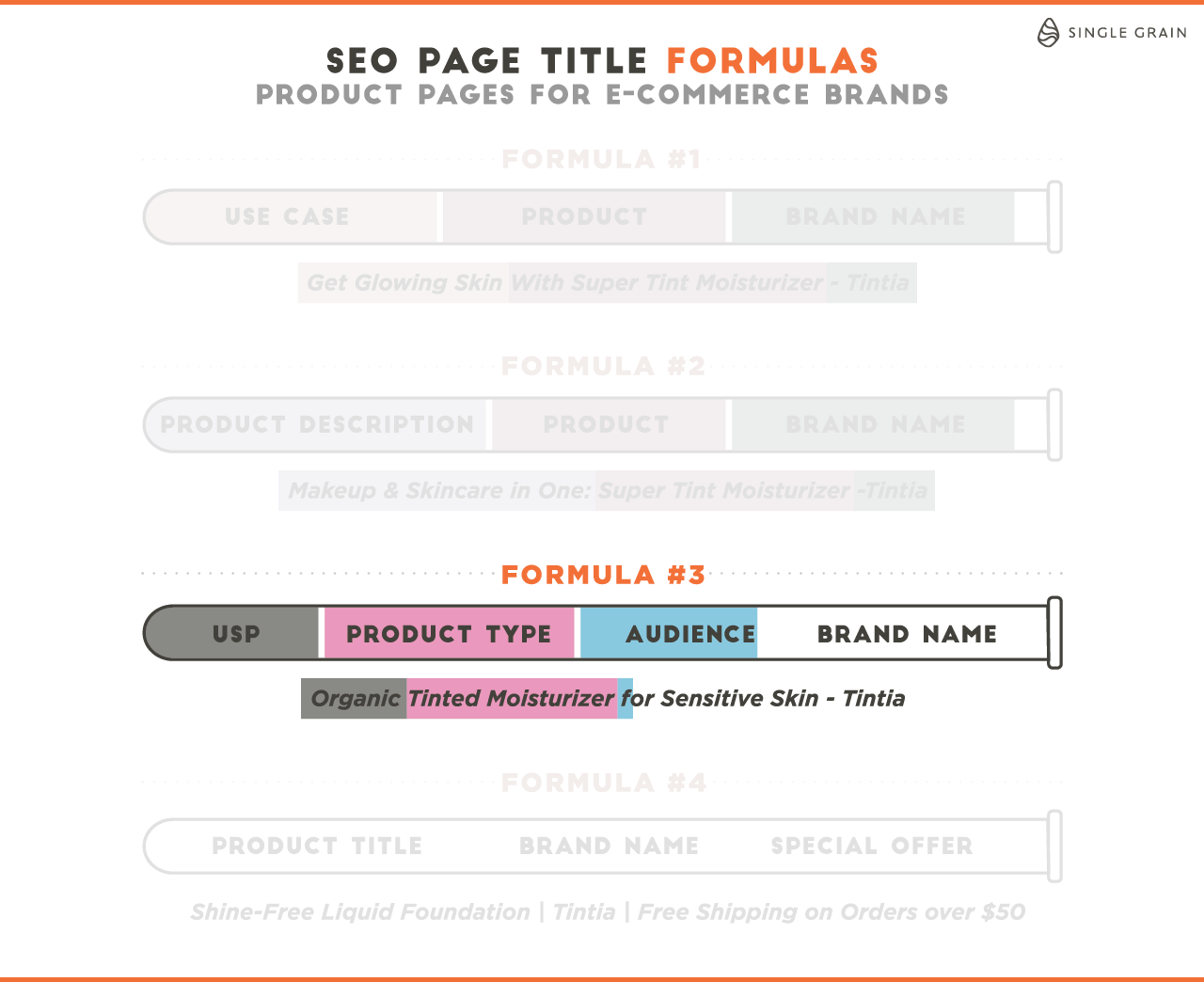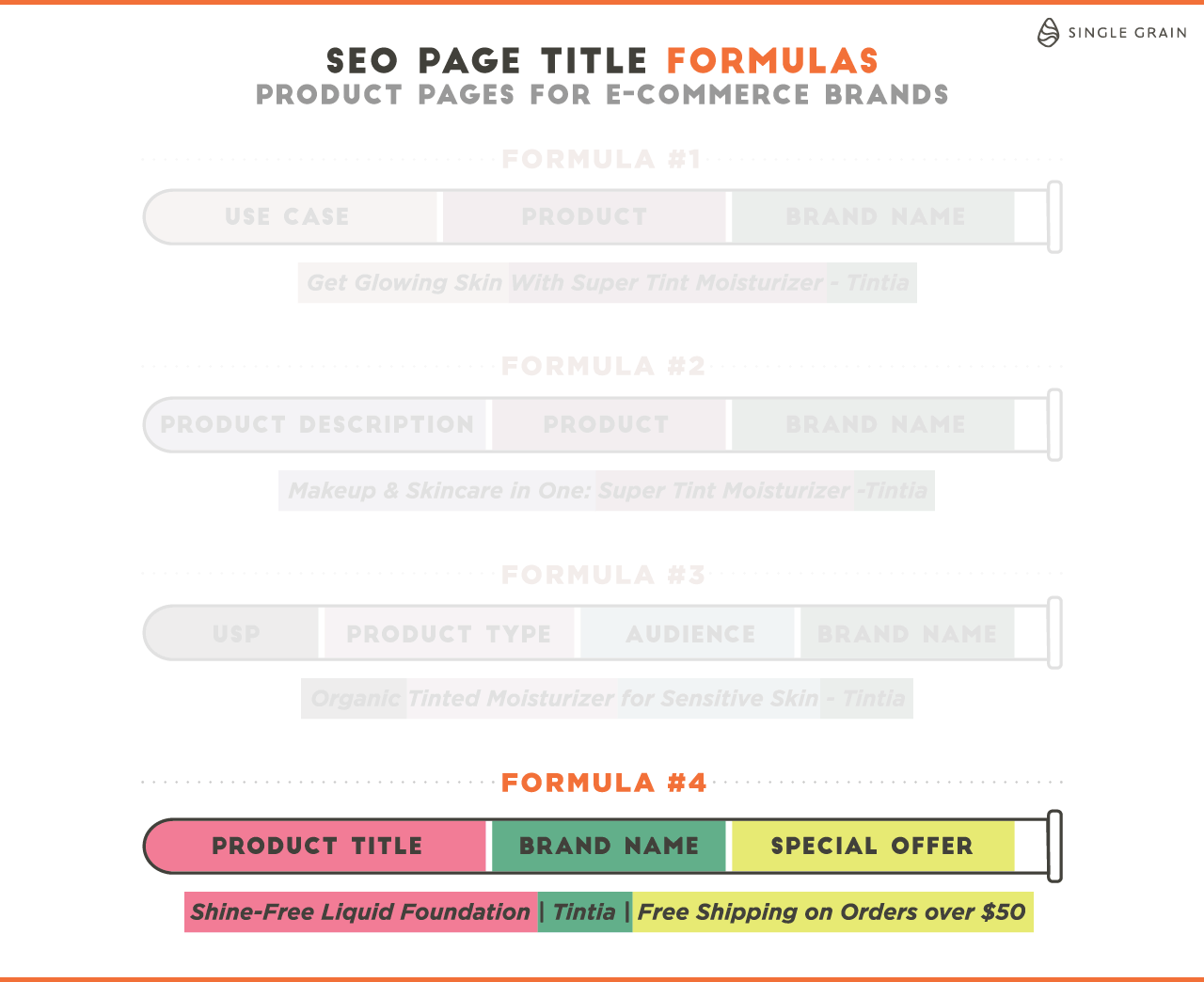
If you need help, this article provides SEO page title formulas for different types of pages to help you improve your blog post ranking:
Get My Free SEO Marketing Plan
9) Repurpose and Refresh Your Old Content Regularly
If you’re struggling to find the motivation to write a long-form blog post, then why not just expand an existing page from, say, 1,200 words to 2,000?
Existing content already has authority and, in some cases, an established readership. Rather than creating a new post from scratch, it can be much simpler to boost an existing post’s performance in the search results by refreshing it with updated information and extra content.
So how do you choose which content to update?
The best candidates for content refreshes are time-sensitive content (in other words, subjects like SEO that are constantly evolving), as well as posts that are getting some organic traffic but have the potential to get much more.
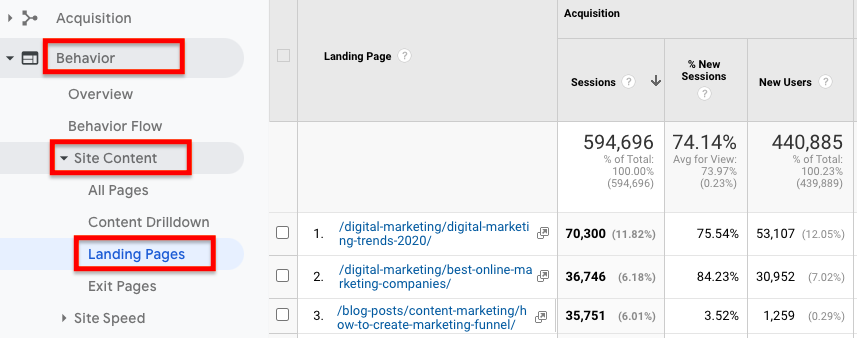
You can find out how much traffic your content is getting in the Landing Pages section of Google Analytics. Just go to Behavior > Site Content > Landing Pages:
Once there, change the segment you’re viewing to “Organic Traffic” and filter the results using your search bar. For example, if you want to view traffic to content that lives in the /blog subfolder of your site, you just need to put /blog in the search bar.
Once you’re ready to update your older blog posts, you can follow the Single Grain updating guidelines:
- Rewrite the intro and conclusion
- Delete/combine any weak sections
- Research and write as much as you feel would add to the value of the piece
- Update any stats/facts/quotes and make sure all links to sources are no more than ~2 years old
- Replace any outdated or irrelevant images
- Replace any examples/case studies with new, current ones
Dive Deeper:
* 9 Ways to Repurpose Your Old Blog Content
* Do You Really Need to Write 1,890-Word Blog Posts to Rank on Page 1?
* Why You Should Update Content – Or Risk Losing The Traffic You Have [Case Study]
10) Create Videos and (Why Not?) a YouTube Channel
You’ve seen that you need to increase your dwell time. What better way to do so than by using video?
According to a Biteable survey:
- 60% of businesses use video as a marketing tool.
- 74% of marketers say video has a better return on investment than static imagery.
- 49% of marketers say that video helps them engage their audience.
- 52% of marketers say that video helps them build trust with potential customers.
Besides increasing visitor engagement, video can also help you get more organic traffic from the Suggested Clips section:
Until recently, Google only ranked YouTube videos in the Suggested Clips, but with the help of the new Seek and Clip data structures, marketers can now rank videos from any site.
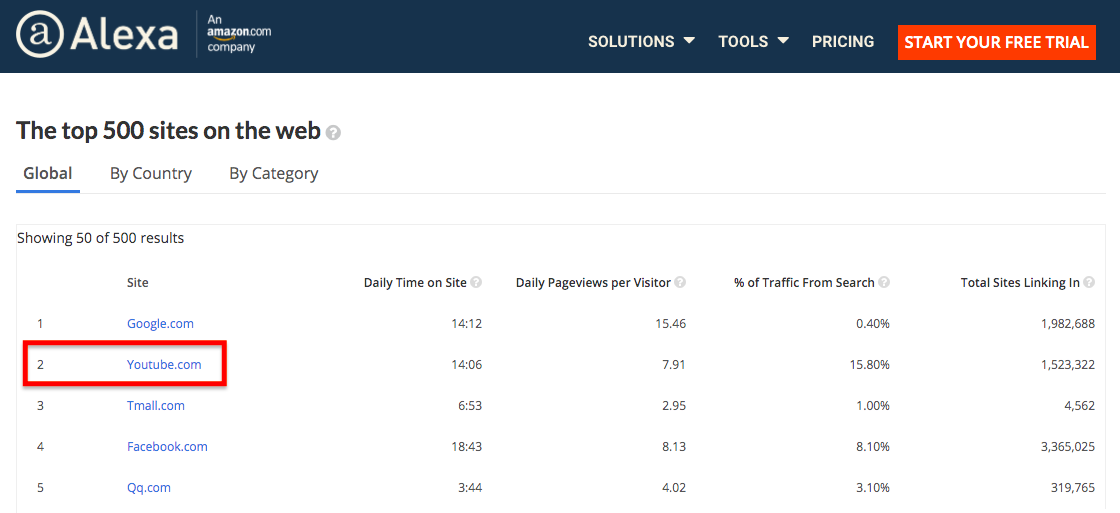
You can also use the videos you create to launch your own YouTube channel, which is:
- The most popular video site on the Internet, with 2.3 billion monthly active users watching 1 billion hours of video every day
- The second-most popular social media platform
- The second-most popular website
Dive Deeper:
* 17 Types of Video Content That People Actually Want to Watch
* How to Make a Video That People Will Watch Til the End
* 20 Pre-Production Tips to Create Successful Video Content in 2020
11) And Don’t Forget About YouTube SEO
YouTube is still the second largest search engine in the world, so optimizing your YouTube videos is a great way to ensure that they are seen by as many people as possible.
SEO doesn’t just mean Google!
If you want to drive more organic traffic to your website from YouTube, then you need to optimize your videos for both YouTube and Google.
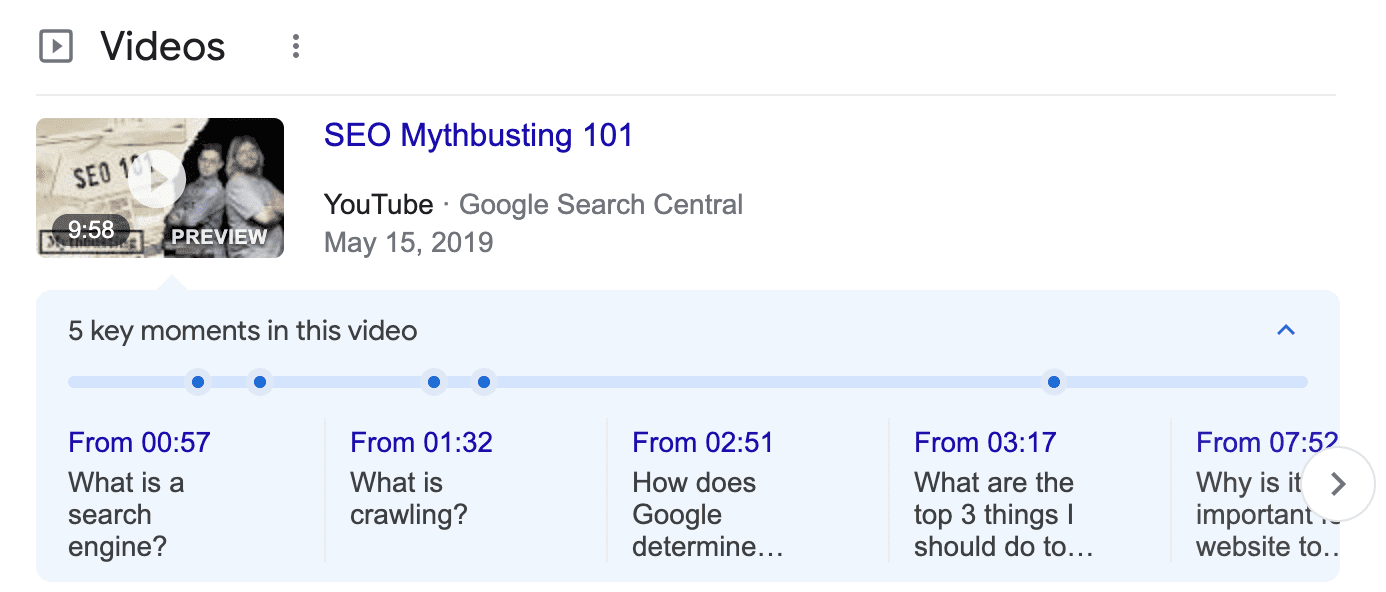
Find a keyword that shows YouTube videos in Google SERPs. If it shows up in Google’s search results, then you will be able to rank the keyword on both search engines:
The subjects that generally tend to have videos are:
- How-to’s
- Product reviews
- Tutorials
- Fitness
This means you need to use these relevant keywords in your video title, description and tags. Keywordtool and Ahrefs are two tools that make it easy to do keyword research for Google, YouTube, Amazon, Bing, and many other search engines:
You should also create transcripts of your videos and include them on your website. This will help Google index your video content and make it easier for people to find your videos in the search results.
To help increase views and subscribers on YouTube, use tools like:
Here are some quick tips for optimizing your YouTube videos for SEO in 2023:
- Use relevant keywords in your video title, description and tags.
- Create transcripts of your videos and include them on your website.
- Promote your videos on social media, email and other websites.
- Use YouTube ads to reach a wider audience.
- Make sure your videos are high quality.
- Optimize your videos for both YouTube and Google.
- Use annotations and cards in your videos.
- Create a strong call to action.
- Use engaging thumbnails.
- Conduct keyword research.
By following these tips, you can optimize your YouTube videos for SEO and improve your chances of ranking higher in the search results.
And don’t forget to promote your videos on other channels, such as social media, email and other websites.
Learn More: The Complete Guide to YouTube SEO
12) Invest In Your Content (and Backlinks)
Link building is and will always be the core of Google’s ranking algorithm. And what is possibly the best way to get backlinks on scale is content.
Content creation is an investment.
In the old advertising days, companies invested in radio, newspaper and magazine ads (they still do, by the way). They also invested in brochures, billboards and trade shows booths.
Content marketing works the same way. You need to invest in creating thorough, useful and unique content that serves your visitors’ needs. We’re not talking about 500-word articles. We’re talking about creating data-driven content.
Data-driven content focuses on creating content backed up by info gathered through quantitative or qualitative research. The research can be done by the company responsible for creating the content or a team of scientists. Articles that merge personal experience with scientific research and data offer the reader an authoritative solution.
Not only does this type of content increase your visitor engagement, but it will increase the number of links you will acquire. Just look at this article; we have linked to many sources that show useful data about different aspects of SEO and digital marketing. The same can happen to you if you create data-driven posts.
To make your data-driven content even better, create images and graphics that visualize the info described in it. One study has shown that humans are more likely to believe in claims about a new drug if they are accompanied by graphs and other data — even if the data adds no new information whatsoever to the claim.
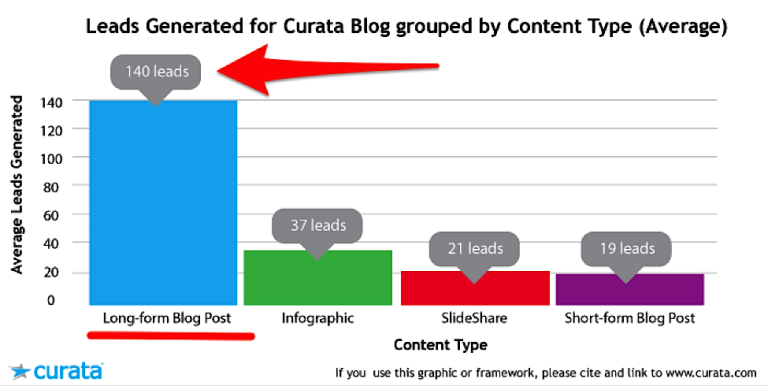
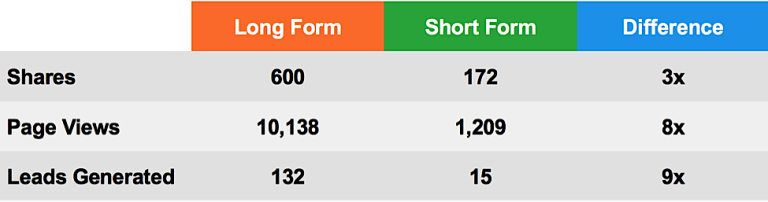
For example, Curata’s use of data-driven content generated 7x more leads than other content types:
And in another study, they discovered that in-depth, data-driven posts received 9x more leads:
Dive Deeper:
* How – and Why – to Build a Backlink Portfolio
* The Skyscraper Technique: How to Build High-Quality Backlinks to Your Content
13) Make Your Content More Visual
Humans like visual content; we are simply wired for it.
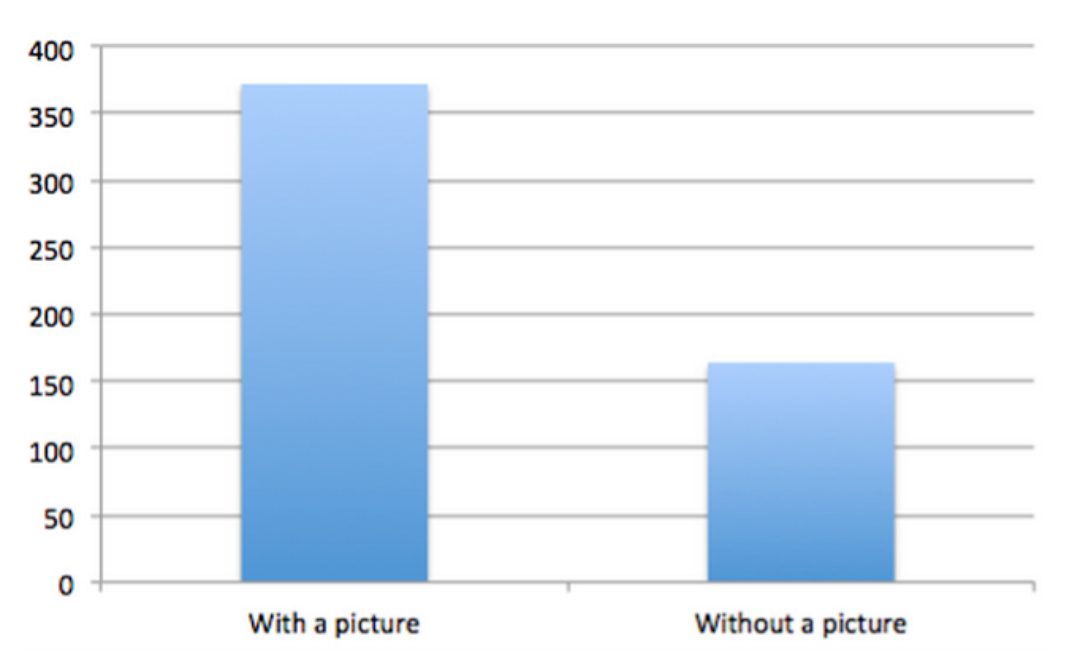
For instance, Facebook posts with images receive 230% more engagement than posts without images:
And for web pages, visual content gets 94% more views than non-visual content:
The most common image types that tend to attract links are:
- Graphics
- Infographics
- Photos
- GIFs
With the help of design tools like Canva, you can easily create your own professional-level graphics. Alternatively, you can use cheap freelance designers on sites like Fiverr and Upwork.
What’s more, people will recognize the effort you put into creating the visuals your content has, which is more likely to get you more inbound links. And besides improving your content, you can rank your images in Google Images, the second largest search engine in the world.
Image SEO requires optimizing your images’ alt-text and their name:
The alt-text is a tag that you give to your images so that Google’s crawl bots can “read” what the image is about. In it, you should include a brief description of the image and a keyword. The name works the same way: you describe what the image is about. So if you have an image of a black cat, your image name should be “black-cat.jpg.”
Dive Deeper: Overlooked SEO: Optimizing Images and Video for Search
Get My Free SEO Marketing Plan
14) Target Local Searchers with Landing Pages and Listings
Here’s some shocking news: 46% of all Google searches come from people looking for local information. That could include:
- Local shops
- Opening hours
- Telephone numbers
- Addresses
For brick-and-mortar business owners, local SEO is a must.
Here are three effective SEO techniques to capture potential customers who live nearby. After all, 72% of people who perform a Google search for local businesses online end up visiting stores within a five-mile radius!
A) Double-Check Your Directory Listings
As powerful as search engines like Google or Bing may be, they still can’t be everywhere at once and sometimes have to rely on additional information from local data sources.
These sources gather, aggregate and submit relevant data for area businesses — information from physical directories (like Yellow Pages) or scanning business registrations. Google then uses these data aggregators to fill in information gaps in their own databases, and will also cross-check information to make sure facts are up to date.
Problems arise when aggregators collect out-of-date data, leading Google to list the wrong information, such as an old address for your business or a disconnected phone number.
That’s why it’s critical to ensure that your physical contact information is current on every online listing you’ve created, including:
- Google My Business: Because Google is the largest search engine, always start with Google My Business, a free-to-use listing service — and update your data accordingly. Be sure to include important details like extra locations, your latest opening hours, and what forms of payment are acceptable.
- Local Directory Management Service: Companies like Moz Local and Yext carry out the painstaking work of scanning countless local directories, interacting with data aggregators, and correcting outdated information.
- Build More Directory Listings Using Local Data Aggregators: Now that you’ve got the information down to a T, roll that out by using a local data aggregator like Bright Local:
From that point on, local search listings should be accurately and automatically updated by your management service. Oh, and remember to change all local listings if something changes — particularly when you move office, switch telephone numbers or are closed for a holiday!
Dive Deeper: The Complete Guide to Google My Business
B) Build and Optimize Local Landing Pages
Let’s think about the search terms people use when they’re looking for local services. Chances are, they look something like this:
- “SEO services in Los Angeles”
- “Best blow dry in Manchester, UK”
- “Where to buy candles in New York”
The only way to make sure you’re reaching the shortlist of Google’s SERPs is to actively target those keywords on your website — preferably with a local landing page.
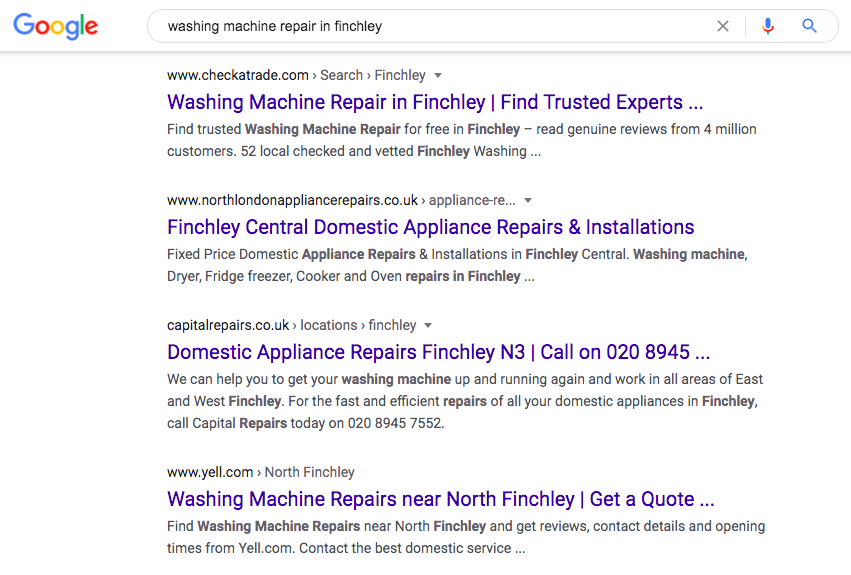
Just take a look at top organic results being shown for a local keyword:
Notice how all the results belong to the Finchley area rather than a home page or general “washing machine repair” service page. You need to create these types of landing pages by:
- Doing keyword research to find local keywords relating to your product or service.
- Creating a new page on your website and optimizing it for those local keywords. That includes mentioning the phrase in your meta title, meta description, page title, heading tags, image alt text, and on-site content.
- Building links from local directory listings to that page to strengthen location-based keyword rankings (e.g., if you’re creating a landing page for London, build links from London-based directories to the landing page’s URL).
Dive Deeper: The Ultimate Guide to Creating a High-Converting Landing Page
C) Technical SEO for Local Search
Carrying out technical SEO for local search is a similar process to that discussed earlier, but here are some useful terms and techniques to ensure that you optimize your business for local searches.
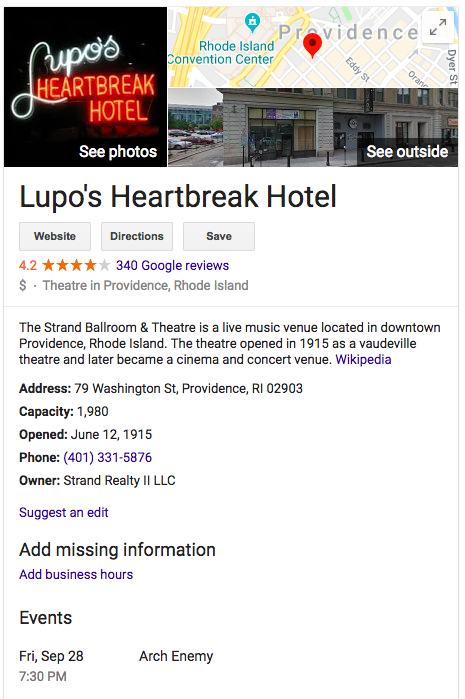
Schema markups are brief snippets of data that provide extra information to users and search engines. Best of all, schema markups don’t require any coding knowledge and can be inserted through Schema.org, a rare collaboration between Google, Yahoo and Bing.
Schema is used on a listing that gives local searchers extra information about the venue’s hours, location, general information and more, without actually visiting the page itself:
If you want to go a step further, you can also include a JSON (Javascript Object Notation) injection through Google Tag Manager. With Google Tag Manager it’s easy to combine schema and JSON to further boost the strength of your schema, resulting in a higher CTR and visibility and without having to spend precious time coding.
Granted, the learning curve is a bit steep for those who aren’t familiar with Javascript or any other basic programming language, but once set in place, JSON injections can help execute and put structured data in place simply and efficiently.
Dive Deeper: The Complete Guide to Local SEO
15) Focus on High-Intent Keywords
Traditional marketing thinking is that you should start with top-of-funnel informational content and work to educate and nurture your audience. That still holds true to an extent, but the great thing about search engine marketing is that you don’t have to be the one to do the nurturing.
There are lots of people out there who are already close to the bottom of the funnel. They’ve gone through a process of education and now their search intent suggests they’re almost ready to make a buying decision.
Broadly, search intent can be categorized into:
- Informational
- Navigational
- Commercial
- Transactional
Reboot provides a nice summary graphic using a golf retailer as an example:
Of those, commercial and transactional can be considered high-intent keywords. If you choose to focus your content efforts on those areas, you can:
- Be more aggressive with CTAs (e.g. “get a quote” instead of “download this cheatsheet”)
- Expect a higher conversion rate
- More accurately attribute leads & revenue to your content
If your goal is a short or medium-term ROI on your SEO and content efforts, high-intent keywords are the way to go.
Dive Deeper: How to Create Intent-Based Content to Improve Conversions
16) Implement E-A-T Best Practices
In the world of SEO, E-A-T stands for Expertise, Authority and Trust. It’s an additional ranking factor that aims to reward content written by a genuine expert, thereby reducing the chance that untrustworthy resources will rank.
In Google’s Quality Evaluator Guidelines, they explain that E-A-T applies differently to different topics. For example, a YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) niche, E-A-T is absolutely critical. YMYL refers to topics like financial advice, or medical advice.
The standards required are different, though. If you’re writing a software review, then being an experienced user of that software could be enough. The important question to ask is: Does this author have the knowledge and experience to be offering advice about this subject?
Here are three quick tactics you can implement to prove to Google (and your users) that your content authors have the necessary expertise:
A) Publish High-Quality “About” Pages and Author Bios
Your “About” page is your chance to boast. Tell readers (and Google) why they should listen to what you have to say. Consider detailing:
- Formal qualifications like a degree or certifications
- Your career experience
- Testimonials and case studies
- Your speaking and writing experiences
B) Implement a Robust Content Review Process
In order to be trustworthy and authoritative, your content needs to be up to date and accurate.
The frequency at which you update content might depend, once again, on the topics. For fast-moving trends like pandemic news, you may need to review daily or weekly. For YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics, like finance and medicine, you may need to check every 3-6 months that your advice is still accurate.
For other topics, yearly may be enough. You can judge this case by case.
Also, be sure to vet any sources that you link out to. Make sure that they, too, are updated, reputable sources.
C) Build More Backlinks
The more backlinks you have from relevant authoritative websites in your niche, the more it’ll support your E-A-T credentials. The same goes for having brand mentions on credible sources (even unlinked mentions).
If others in your industry are citing your work as a resource, it’s a good sign you’re an authority to be trusted in that niche.
So invest some time into creating great content and building the right relationships, and you’ll earn quality links.
Dive Deeper:
* 4 Ways to Signal to Google that You’re an Expert Content Creator
* The Ultimate Guide to Link Building with Content for SEO
* Google’s Search Quality Rater’s Guidelines: Ensure that Your Site Gets a High Quality Rating! [infographic]
17) Optimize Your Internal Links
Internal linking has always been important for SEO, and it continues to be for the coming year. Optimizing internal links for your priority pages can be a low-cost SEO technique that doesn’t need to take up great amounts of time and resources.
There are two primary purposes to internal linking:
- To pass and distribute the value of your backlinks to your pages
- To help users navigate to the content most relevant for them
Here are three quick tips and strategies to make the most out of your internal linking:
A) Push TOFU Readers Further Down the Funnel
Most established websites tend to have a lot of top-of-funnel, low-intent traffic from informational keywords. It’s unlikely you’ll have any success trying to drive customers directly from this type of content.
Instead, one of the things you can do is use internal links to push people to the next step of the funnel. Here’s an example. Let’s say you have traffic from a definition keyword like “what is brand awareness”. What’s the next logical content?
- What is brand awareness
- Benefits and importance of brand awareness
- How to measure brand awareness
- Software for measuring brand awareness
This is a simplified illustration of the consumer decision-making process. It’s not likely that someone will really Google “what is brand awareness” and end up buying software for measuring brand awareness all in the same session.
That said, it’s a best practice to continue adding internal links in TOFU and MOFU content that push the reader closer to pages that actually convert and generate revenue.
Dive Deeper: What’s the Right Content for Each Stage of the Marketing Funnel?
B) Use Clear and Descriptive Anchor Text
If the purpose of internal links is to guide search engines and users around the site, then your text anchors need to be descriptive.
If you have unclear anchors like “see more,” “learn more,” “here,” and so on, they’re less likely to be beneficial. Make it obvious where the click is going to lead.
In addition, make sure that the anchors differentiate between pages, too. For example, let’s say you have all of these pieces of content on your blog:
- Fashion newsletter examples
- Fitness newsletter examples
- Travel newsletter examples
In that case, avoid using a generic anchor like “newsletter examples,” which is confusing because it could be relevant for several different pages. The exception might be if the page title or closest subheading give clear context (e.g. the entire article is about fitness newsletters). It’s still safer to use the full descriptive anchor, and requires very little additional effort.
Dive Deeper: How to Implement Internal Linking for SEO (Step-by-Step)
C) Limit the Number of Internal Links
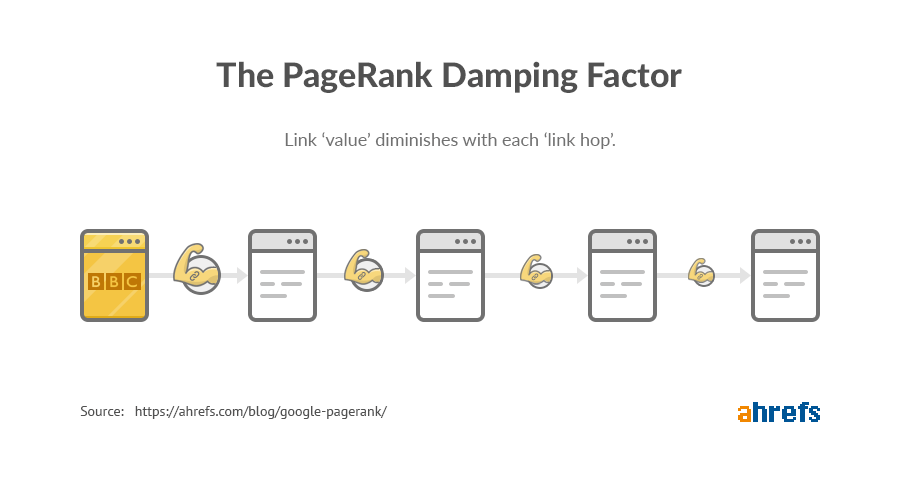
Google recommends using a reasonable number of internal links, though they don’t provide any real guidance as to what that means.
When you add internal links, you’re indicating to Google which of your pages are important. Every page can’t be equally important, right?
In theory, every additional internal link that you add will dilute the amount of “PageRank” (no longer an official metric, but the concept is still relevant) passed to other pages receiving links. Here’s an illustration from Ahrefs to visualize:
Dive Deeper:
* How to Rank Your Brand-New Website When You Don’t Know SEO
* 9 Quick SEO Tactics That Only Take 10 Minutes to Implement
* The Complete White Hat SEO Guide: Google-Validated SEO that Works like Magic!
Keeping Up with SEO
SEO is an ever-evolving field, so it’s important to keep up with the latest changes and trends. To stay on top of these changes, make sure to spend time on the fundamentals of quality content creation, technical trends, backlinks and internal links, site speed, and schema.
However, you don’t need to implement every single new technique immediately. Just focus on a few SEO strategies that make sense to your business at first, and you’ll see a big difference in your site’s click-through rates, engagement and, of course, rankings.
Hopefully you learned all about effective SEO techniques to improve your website! But if you just want an expert SEO agency to do it for you, click here.
SEO Techniques FAQs
What is SEO and how does it work?
Search engine optimization, also known as SEO, is the process of optimizing a web page to rank in a search engine’s result pages (SERPs).
To make SEO work, a web page must be properly crawled and indexed by Google. For every search query, Google’s algorithm weights all the pages that seem relevant to it and authoritative, and organizes the results accordingly.
SEO marketers optimize a web page around a search query (a “keyword”) by adding the latter in its title tag, headers, alt-text, and URL. They also make sure the keyword and its variants show up several times throughout the page.
To build authority, SEO marketers build links from external sites that point to their page (known as “inbound links”) from sites with high authority as measured by SEO tools like Ahrefs and Moz. Popular authority metrics include “Domain Authority” (or “Domain Rating”) and “Page Authority” (or “Page Rating”).
How do you develop an SEO strategy?
To develop an SEO strategy, you need to structure it around four main categories:
- The keyword research side, which includes finding keywords that have a mix of high search volume, high intent, and high relevance for the website’s value proposition
- The technical side, which includes creating a sitemap, increasing the website’s loading speed, and fixing any crawlability and indelibility issues
- The on-site side, which includes optimizing each page around a keyword
- The off-site side, which includes building a strategy to acquire high-authority links
What are the top three SEO strategies for 2023?
From the SEO techniques we shared in this article, the main ones to consider are:
- Optimizing your page experience: Make sure your Core Web Vitals are all within the thresholds Google defines. Also, take care of the other three aspects that Google cares about: mobile-friendliness, secure domains (buy an HTTPS certificate), and a non-intrusive user experience.
- Leverage AI content writing tools: AI-powered writing tools can help you create high-quality, keyword-optimized blog posts at scale. This SEO strategy for content marketing is becoming increasingly popular as it can help you save time and money.
- Optimize your existing content: You can use a tool to boost your organic CTR and get a higher chunk of organic traffic. You also need to update your old content regularly.